
Since researchers have found more strokes occur in the left side of the brain – which may impact the functionality of the right-hand side – people who are right handed might be more likely to suffer loss of functionality after a stroke.

This is important as the right hand side of the brain controls the left side of the body and vice-versa.
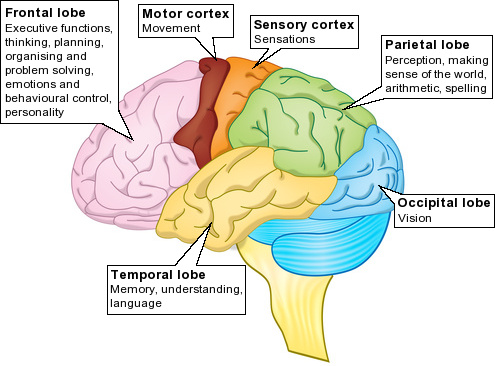
It’s well known that more strokes – where blood supply to areas of the brain are interrupted – happen on the left hand side of the brain. There’s a correlation between dominant hand and stroke likelihood. Therefore, approximately 14 millilitres are delivered to the brain per heartbeat, which is essential for getting oxygen to the brain cells. For the average male, around 70 millilitres of blood pump round the body per heartbeat. The brain receives between 15-20% of blood from the heart at rest – but many factors can effect this, including age, gender, and weight. Maintaining brain function, like with all living tissues, relies on the supply of oxygen from blood. About 20% of the body’s blood goes to the brain However, just like sensory information, motor actions can happen involuntarily, like breathing, or the muscles moving food through our gastrointestinal system. For example, information about the position of your muscles and joints is always being sent to the brain – but we rarely notice this until it becomes uncomfortable, or you need to adjust your position.īut when it comes to outgoing motor information – including voluntary actions we control, such as picking something up – we are aware of the function. Sensory information is what flows into the brain, and motor information is what flows out of it.Īlthough the brain is always receiving this information, we’re often unaware of it as it goes areas of the brain that process “unconscious” information. This information is controlled by two pathways, which keep everything in check. The brain is constantly receiving a flow of information. Knowing which parts perform which tasks is important both for research, and when performing surgery. For example, an area in the frontal lobe called Broca’s area is specifically involved in language production and comprehension.īy scanning the brain, scientists can measure when and which areas become more active in the brain by looking at which areas experience an increase in blood flow, which delivers the extra oxygen the area needs to function or perform a task. These are individual regions of a certain lobe that’s responsible for specific functions. The lobes are further divided into functional regions. When light enters your eyes, it’s transmitted by nerves to this region and converted to an image that you “see”. The occipital lobes are involved in visual processing. The temporal lobes also receive information relating to sounds – including the language we hear – as well as in memory processes. These include sensory and numerical processing, as well as visuo-spatial information – which is needed for movement, depth perception, and navigation. The parietal lobes are involved in a mixture of functions. It also helps us make memories, and learn to regulate emotions and behaviour. It’s involved in cognitive processes such as reasoning, learning, creativity, attention and controlling muscles used for movement and speech.

The frontal lobe is often associated with what “makes us human”. The parietal lobes are located in the middle and the occipital lobes are at the back of the head. The frontal lobes are located near the front of the head and the temporal lobes are just beneath them. The brain is divided into four pairs of lobes on each side of the head. But different parts of the brain are responsible for different functions. It’s always activeĮven when we’re sleeping, our brain is always active. But despite how important our brains are, many people still know very little about it. Not only does it control basic life functions like breathing, organ function, and movement, it’s also behind more complex processes – everything from thought, controlling our behaviour and emotions, and creating memories. Our brain is the most complex organ in the body.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
